Shaping Ideas into Reality
3D printing is both a new age as well as a reliable manufacturing process for over a few decades. This technology was first coined in 1986 but since then, it has been enhanced and developed expanding capabilities.
Also known as additive manufacturing, it is a revolutionary technology that creates a three-dimensional object layer by layer. It has gained significant popularity in various industries due to its versatility and numerous applications.
3D printing or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model.
3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGIES
We provide a comprehensive selection of 3D printing technologies tailored to our customers’ specific requirements. Our cutting-edge 3D printers enable us to create top-notch objects using a diverse range of materials.
Our skilled designers and engineers possess extensive expertise in Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM), ensuring that your parts are optimized for the highest quality results using our state-of-the-art machinery. Whether you need a prototype, spare part, or end-use product, we have both the proficiency and equipment to transform your ideas into reality.
Our range of printing technologies include:
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a popular 3D printing technology that uses a filament of thermoplastic material to create objects layer by layer. The object is finished when all the layers are completed FDM technology offers several advantages, including its affordability, ease of use, and versatility in material options. It is widely used in various industries, including prototyping, product development, education, and hobbyist applications.
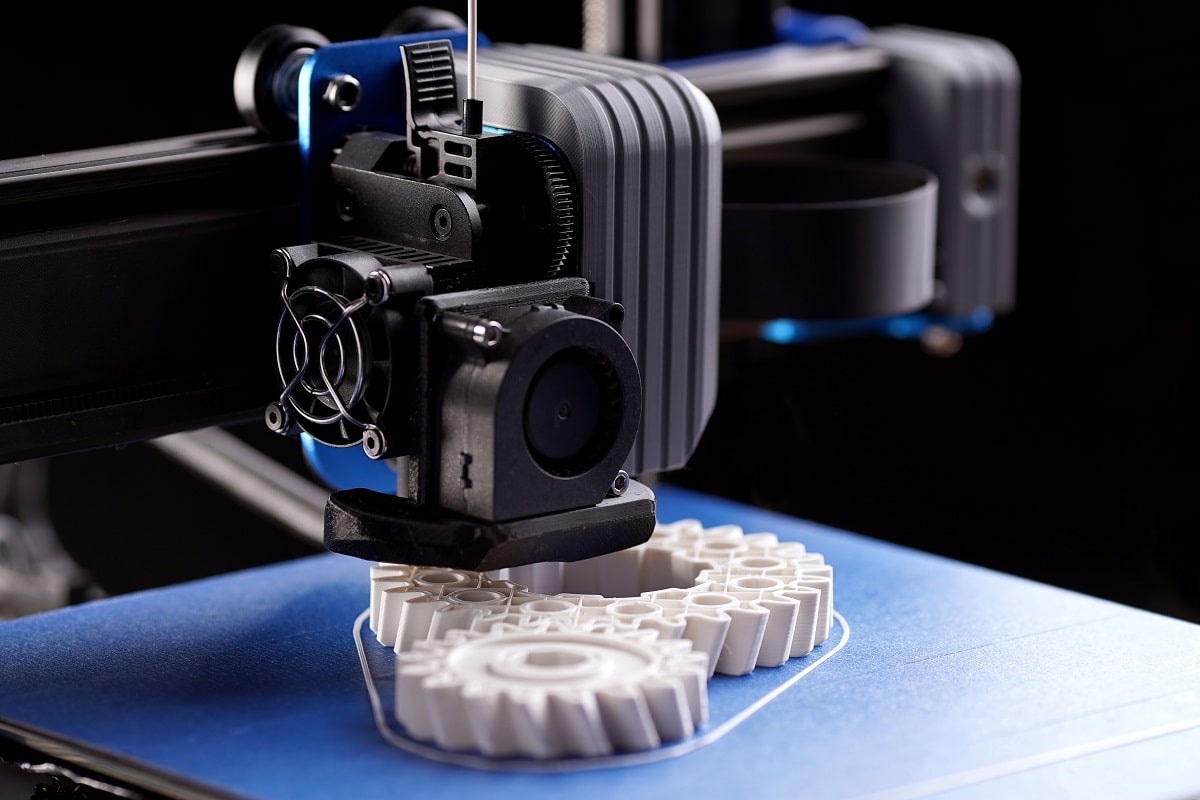

Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a 3d printing technology. This technology uses a laser to fuse powdered materials from polymers to metal to create objects layer by layer. It is different from other 3D printing technology that use melting and extrusion processes.
In short SLS technology solidifies powder material to create objects using a laser.
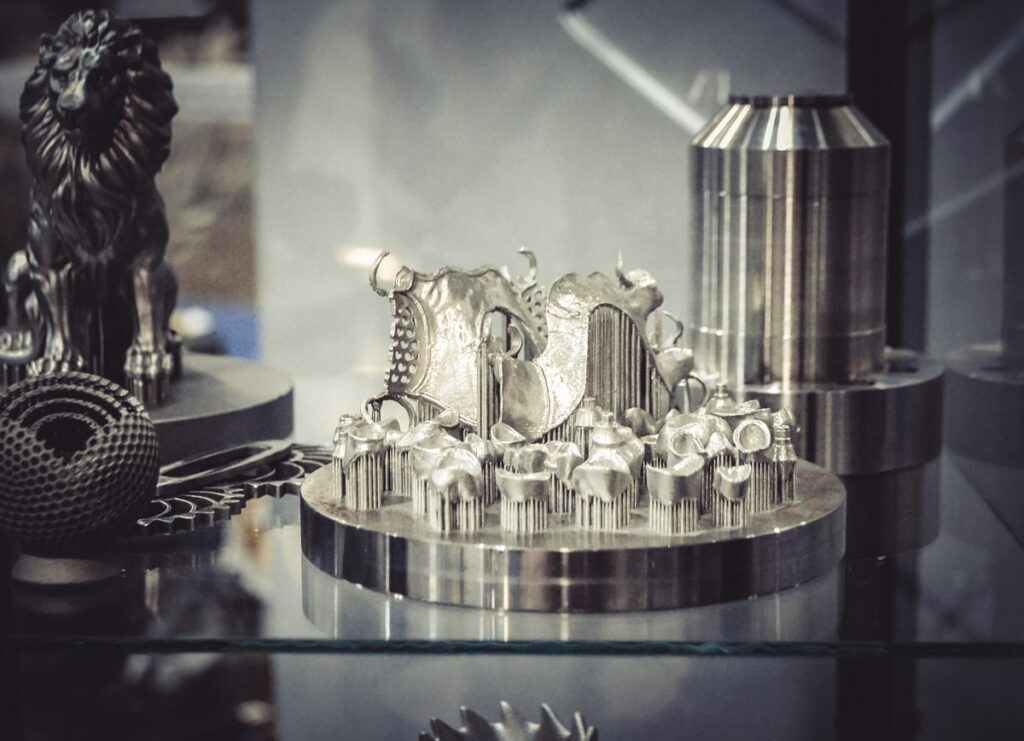

Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA short for Stereolithography, was one of the first 3D printing technologies used. It uses photosensitive liquid resin and a laser to create solid objects with high precision. A series of overlapping beams from a laser are directed on the surface to form a precise solid surface.
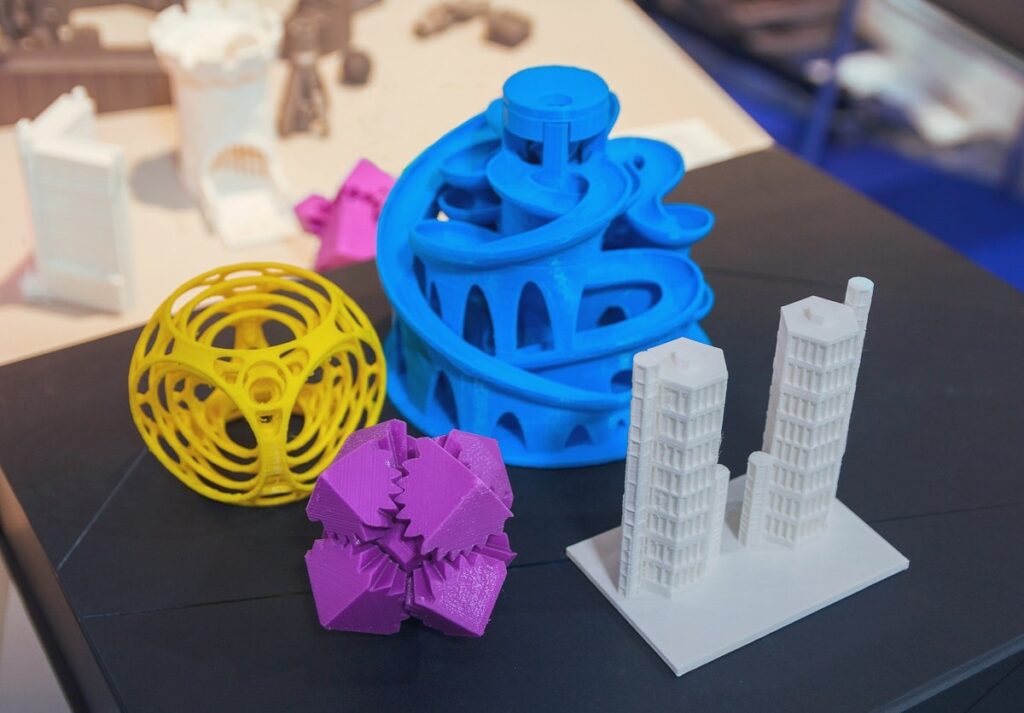
Key Uses
- Prototyping: 3D printing is widely used for Prototyping, also known as sample making. This technology enables a quick turnaround time for model testing and sampling before the mass production.
- Manufacturing: 3D printing or additive manufacturing is used for product manufacturing as well. From complex to simple, it helps in making customized products reducing wastage and costs.
- Education and Research: 3D printing has enabled research institutes to learn by creating visual aids, anatomical models, and prototypes. They use this technology to make complex components to study and experiment for scientific research.
- Customization and Personalization: A key advantage of 3D printing is that you can manufacture small quantities instead of mass production. These products can be personalized as well as customized as per each unique demand. This is particularly valuable in industries such as healthcare (custom prosthetics) and fashion (bespoke jewelry).
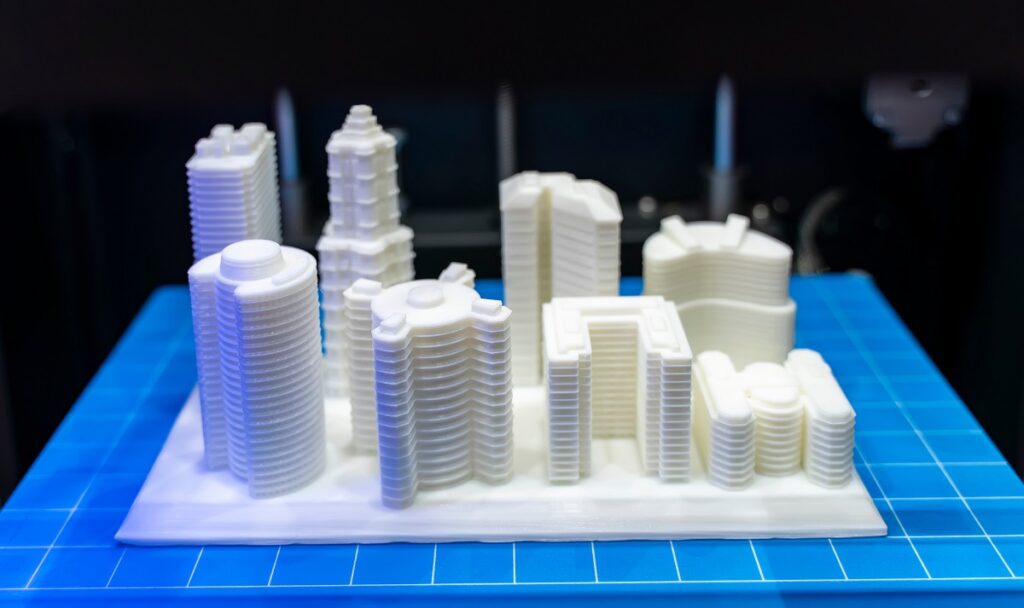
Features of 3D Printing
- Layer-by-Layer Construction: 3D printing technology builds objects / products, by layering. This layering process makes it easier to make complex designs that would be challenging to make using traditional methods.
- Design Flexibility: Additive manufacturing offers tremendous design freedom, enabling the creation of intricate and organic shapes that may be impossible or costly to produce using traditional manufacturing techniques.
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printers can quickly transform digital designs into physical objects. This speed allows for faster iteration and testing, accelerating the product development cycle.
- Material Variety: 3D printing supports a wide range of materials, including plastics and even biocompatible or bioresorbable materials. The availability of diverse materials enables customization & production of objects with specific properties and functionalities.
Materials used are: PP, PLA, ABS, Nylon, Polyurethane, etc. Along with these, food complaint materials are used which are gaining popularity.













